Introduction
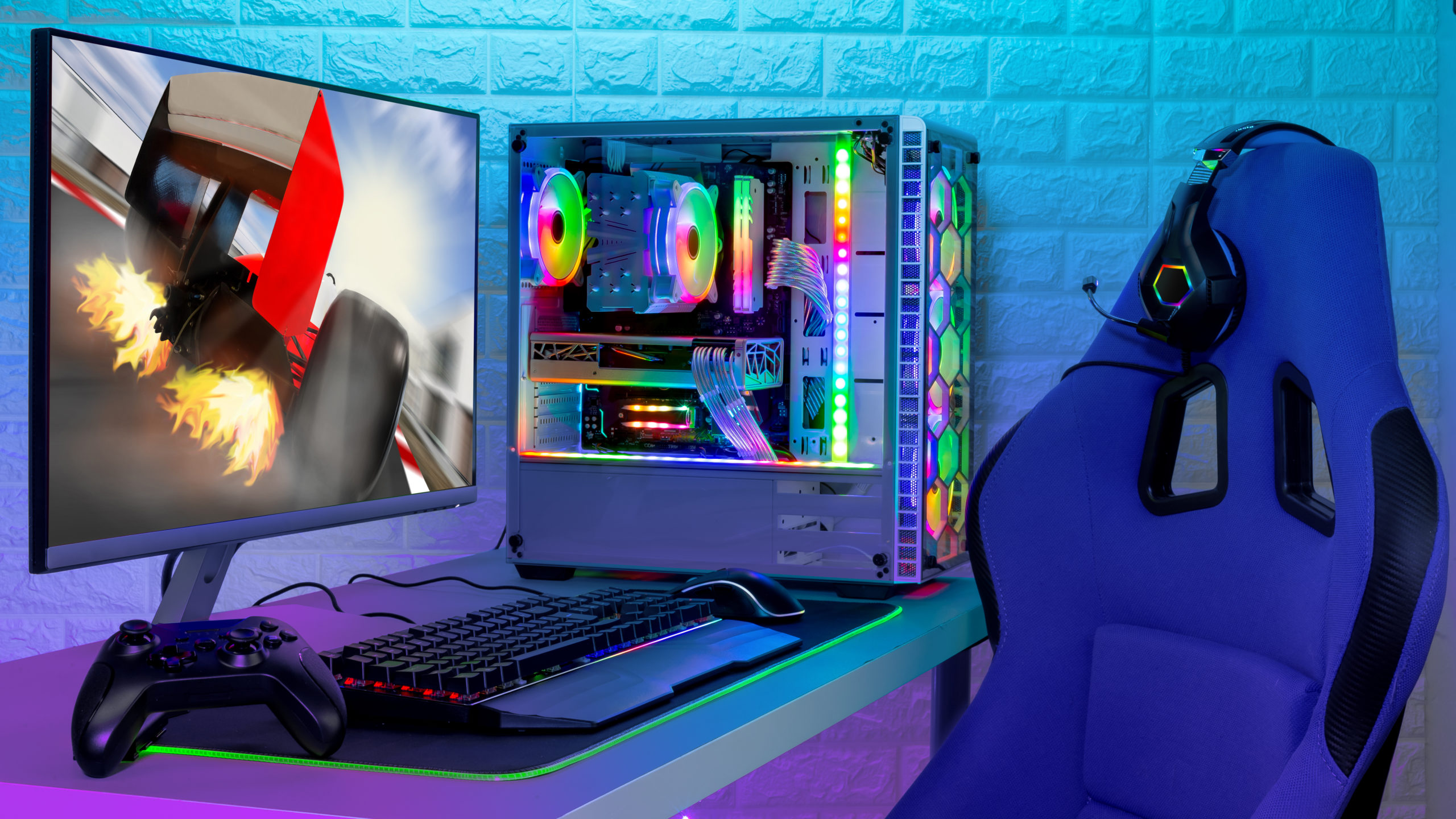
Cloud-based PC gaming is transforming how we experience and interact with video games. As technological advancements accelerate, traditional gaming methods, which often require powerful hardware, give way to more accessible alternatives. Cloud-based gaming, also known as cloud gaming or gaming-as-a-service, allows players to stream games directly from remote servers without the need for expensive, high-end gaming rigs. This shift represents not just a technological leap but also a cultural change in the gaming world, breaking down entry barriers and enhancing players’ overall experience.
In the past, PC gamers had to invest in costly hardware like top-tier graphics cards, CPUs, and other gaming peripherals to enjoy the latest games. This often made high-performance gaming out of reach for many players due to budget constraints or technical expertise. However, cloud-based PC gaming has opened up new possibilities by moving the computational heavy lifting from the player’s device to powerful data centers. The PC game is processed and rendered remotely, with the resulting video streamed to the player’s device in real time. This model makes gaming accessible on a wide range of devices, including low-end PCs, tablets, smartphones, and even smart TVs.
The cloud gaming industry has evolved rapidly in recent years, and major companies such as Google, Microsoft, NVIDIA, and Sony have launched their own cloud gaming platforms. Google Stadia, Microsoft’s Xbox Cloud Gaming, NVIDIA GeForce Now, and PlayStation Now are among the prominent platforms that offer gamers access to a vast library of PC game without the need for physical copies or downloads. These services have made it possible for gamers to play high-quality titles on devices that previously would not have been able to run such PC game. This technological advancement has expanded the gaming audience, creating a more inclusive environment for casual players and hardcore gamers alike.

The Technology Behind Cloud Gaming
Cloud gaming relies on several key technologies to provide players with a seamless experience. At the heart of cloud gaming are data centers, where the hardware responsible for running the games is located. These data centers house powerful servers equipped with state-of-the-art GPUs, CPUs, and storage solutions. These servers handle all the PC game processing, including rendering, physics calculations, and AI, while the game footage is streamed to the player’s device. The player’s input, such as controller or keyboard commands, is sent back to the server, where it is processed in real time.
A fast and stable internet connection is crucial for cloud gaming to work effectively. Since cloud gaming involves real-time high-definition video streaming and rapid input response, latency and bandwidth are major concerns. Latency refers to the delay between the player’s input and the server’s response. Even slight delays can disrupt the gaming experience, especially for fast-paced PC gaming like first-person shooters or competitive multiplayer titles. To minimize latency, cloud gaming providers have invested in developing low-latency streaming protocols and placing data centers in strategic locations worldwide.
Bandwidth requirements are also significant for cloud gaming, especially when streaming PC gaming in 4K resolution or higher. While most cloud gaming services recommend a minimum internet speed of 10 to 20 Mbps for smooth gameplay, higher resolutions and frame rates may require upwards of 50 Mbps. Advances in network infrastructure, including the deployment of 5G and fiber-optic internet, are helping to improve the accessibility and performance of cloud gaming, allowing players to enjoy a more immersive experience with reduced lag and buffering.
Advantages Of Cloud-Based PC Gaming
One of the primary advantages of cloud-based PC gaming is its accessibility. Gamers no longer need to worry about whether their hardware can meet the requirements of a particular PC gaming. With cloud gaming, even users with modest devices can enjoy the latest AAA titles without investing in expensive components. This is a game-changer for gamers who may not have the financial means to purchase a high-end gaming rig or upgrade their system every few years. Cloud gaming democratizes access to high-quality gaming experiences, allowing more people to participate in the gaming community.
Another advantage is the convenience of playing PC gaming on multiple devices. Cloud gaming services enable players to access their games from a wide range of platforms, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart TVs. As long as the device has a screen and an internet connection, it can be used to stream games. This flexibility allows players to switch between devices seamlessly, making it easy to pick up where they left off, whether they are at home or on the go. Furthermore, because cloud gaming services handle all game updates and patches server-side, players no longer have to deal with lengthy installation or update processes. The game is always up-to-date and ready to play whenever the player logs in.
Cloud gaming also eliminates the need for physical PC gaming copies or large digital downloads. In traditional gaming, players often had to wait hours for a game to download or install, especially for large titles that can exceed 100 GB in size. With cloud gaming, there is no need to worry about storage space or download times; games are streamed directly from the cloud, allowing players to jump into the action almost instantly. This has the added benefit of reducing the environmental impact associated with manufacturing and distributing physical game copies, making cloud gaming a more sustainable option in the long run.
Challenges Facing Cloud Gaming
Despite its many advantages, cloud-based PC gaming is not without its challenges. One of the biggest obstacles is the reliance on a fast and stable internet connection. In regions with poor or inconsistent internet infrastructure, cloud gaming may not be a viable option for many players. High latency and slow download speeds can lead to a subpar gaming experience, with issues such as input lag, screen tearing, and buffering detracting from the overall enjoyment. While internet connectivity is steadily improving in many parts of the world, there is still a significant digital divide that may prevent some players from fully embracing cloud gaming.
Another challenge is the subscription model adopted by many cloud gaming platforms. While some services, like GeForce Now, allow players to stream PC gaming they already own, others, like Google Stadia, require players to purchase games separately or subscribe to access a library of titles. For players who are used to owning physical copies of games or purchasing them outright through platforms like Steam, the subscription-based model of cloud gaming may be less appealing. The ongoing cost of subscriptions can add up over time, and some gamers may be hesitant to invest in a service where they don’t have permanent ownership of the games they play.
The quality of cloud gaming can vary depending on the player’s location relative to the data center. While cloud gaming providers strive to minimize latency by placing data centers in key locations, players who live far from these centers may still experience noticeable delays in input response and image quality. This can be particularly problematic for competitive PC gaming, who rely on split-second reactions to perform at their best. In addition, bandwidth caps imposed by some internet service providers can limit the amount of data a player can stream, potentially disrupting gameplay and limiting access to higher resolutions or longer gaming sessions.
Cloud Gaming Platforms: A Comparative Look
Several companies have entered the cloud gaming market, each offering its own unique features and benefits. Google Stadia, one of the most prominent cloud gaming platforms, launched in 2019, promising to bring AAA gaming to a wide audience. Stadia allows users to purchase PC gaming à la carte and stream them directly to their devices, supporting 4K resolution and HDR. Despite initial excitement, Stadia faced criticism for its limited game library and high pricing model, which required players to buy games individually and pay for a subscription. Nevertheless, Stadia’s technology remains impressive, with smooth performance on various devices and integration with Google’s ecosystem.

Microsoft’s Xbox Cloud Gaming, part of the Xbox Game Pass Ultimate subscription, offers a different approach. Rather than requiring players to buy PC gaming individually, Xbox Cloud Gaming provides access to a large library of games for a monthly fee. This subscription model has proven popular with gamers who enjoy having a wide selection of titles without needing additional purchases. Xbox Cloud Gaming is also integrated into the broader Xbox ecosystem, allowing players to seamlessly sync their progress between Xbox consoles and cloud-enabled devices.
NVIDIA’s GeForce Now is another major player in the cloud gaming space. Unlike Stadia, GeForce Now allows players to stream games they already own from platforms like Steam, Epic Games Store, and Ubisoft Connect. This model has attracted a loyal user base, allowing gamers to leverage their existing game libraries without repurchasing titles. GeForce Now also supports 4K streaming and high frame rates, making it an attractive option for gamers who prioritize performance. However, its free tier limits session length and the premium tier requires a monthly subscription to access additional features like extended playtime and RTX (ray tracing) support.
Sony’s PlayStation Now, which predates many other cloud gaming services, offers a library of PlayStation games that can be streamed or downloaded to PlayStation consoles and PCs. PlayStation Now’s library includes both classic PlayStation titles and newer PC gaming, making it an appealing option for fans of the PlayStation ecosystem. However, the service is limited to PlayStation platforms, which may deter gamers who prefer cross-platform flexibility.
The Role Of 5G In Cloud Gaming’s Future
The arrival of 5G technology has the potential to further enhance cloud-based PC gaming by addressing some of the current challenges related to latency and bandwidth. 5G offers faster download speeds, lower latency, and increased network capacity, all of which are critical for a smooth cloud gaming experience. With 5G, players can expect more responsive gameplay and higher-quality streaming, even in mobile environments. This could make cloud gaming more accessible to a broader audience, as players will no longer be tied to wired internet connections or Wi-Fi networks to enjoy high-performance gaming.
In addition to improving the player experience, 5G could enable new gaming content forms. For example, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) games, which require large amounts of data to be processed and transmitted in real-time, could benefit from 5 G’s low latency and high-speed capabilities. As 5G networks expand, cloud gaming platforms will likely integrate more advanced features, further blurring the lines between gaming on dedicated hardware and gaming in the cloud.
The Future Of Cloud-Based PC Gaming
The future of cloud-based PC gaming is bright, with many exciting developments. As internet infrastructure continues to improve and 5G networks become more widespread, the accessibility and performance of cloud gaming will only increase. This will likely lead to a larger, more diverse gaming audience, as players who previously could not afford or access high-end gaming hardware can participate in the gaming ecosystem.
In addition to technological advancements, the gaming industry will likely see continued innovation in PC gaming design, driven by the possibilities of cloud gaming. Developers will have more freedom to create expansive, graphically intensive worlds without worrying about hardware limitations, as powerful cloud servers will handle the burden of rendering and processing. This could lead to the creation of new types of games that take advantage of the unique capabilities of cloud gaming, such as real-time multiplayer experiences on a massive scale or dynamic, evolving game worlds that change based on player input across the globe.
Cloud-based gaming is also likely to impact PC gaming distribution and monetization significantly. As cloud gaming services become more prevalent, we may see a shift away from traditional game sales toward subscription-based models, where players pay a monthly fee to access a library of games. This could change the way games are developed and marketed, with developers focusing more on creating content that keeps players engaged over the long term rather than relying on one-time purchases.

Conclusion
Cloud-based PC gaming represents a significant shift in the gaming landscape, offering players unprecedented access to high-quality PC gaming without the need for expensive hardware. Cloud gaming democratises gaming by leveraging the power of remote servers and fast internet connections, making it more accessible to a broader audience. While challenges such as latency, internet infrastructure, and the subscription model still need to be addressed, the future of cloud gaming is bright. As technology evolves, cloud-based gaming will likely play an increasingly important role in the industry, providing new opportunities for players, developers, and publishers alike. Cloud gaming is poised to become a dominant force in the gaming world with the potential to revolutionize how games are played, distributed, and experienced.